Publication: Chemokine receptor pharmacology through design of fluorescent allosteric modulators
17 September 2023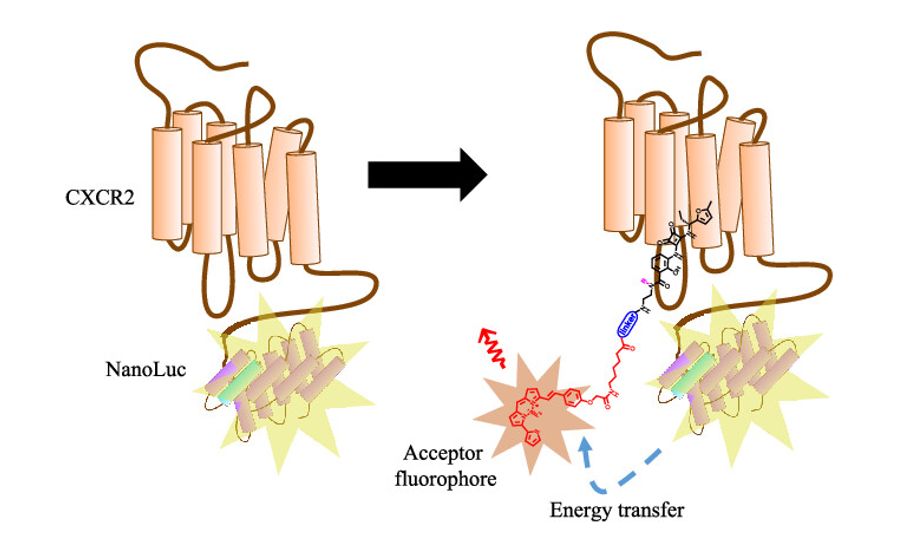
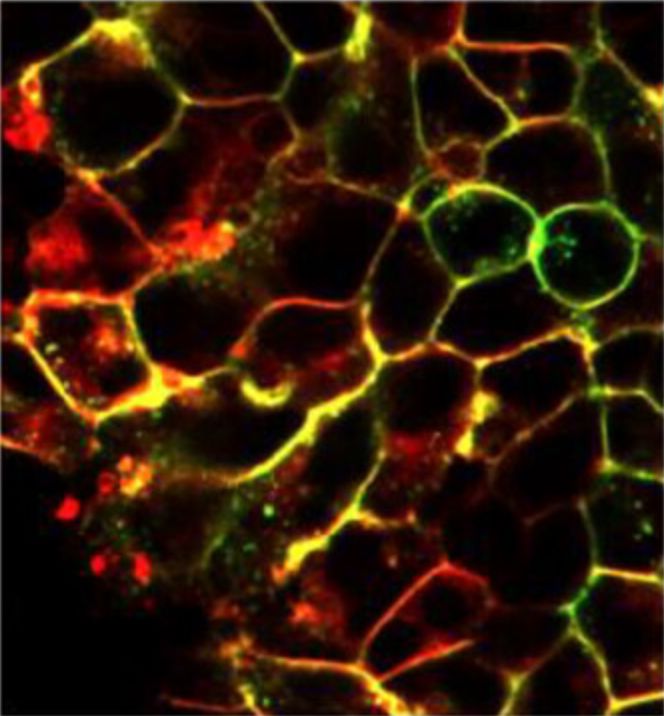 Live cell imaging of compound binding to SNAP-tagged CXCR2-tsNanoLuc HEK293
Live cell imaging of compound binding to SNAP-tagged CXCR2-tsNanoLuc HEK293
Nick Holliday and colleagues at the University of Nottingham have recently published their work on the development of novel fluorescent antagonist probes for the chemokine receptor CXCR2, in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.
CXCR2 antagonists are of potential interest in the treatment of inflammatory disorders and cancers. Unusually, a number of the developed small molecules bind to an intracellular allosteric site on the receptor to exert their inhibitory effect. The team designed novel fluorescent ligands to bind selectively to this site, enabling visualisation of probe binding through fluorescence imaging to CXCR2 expressing cells.
In addition, these probes are suitable for robust medium throughput receptor binding assays using NanoBRET technology. This is a powerful approach to allow direct measurement of allosteric ligand affinities and binding kinetics at CXCR2 and CXCR1 receptors.
Casella BM, Farmer JP, Nesheva DN, Williams HEL, Charlton SJ, Holliday ND, Laughton CA, Mistry SN; (2023). Design, Synthesis, and Application of Fluorescent Ligands Targeting the Intracellular Allosteric Binding Site of the CXC Chemokine Receptor 2. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry